After attending a talk at the GitHub Universe 2016 about Hubot, I felt the need to write a little Go library to speed up my process of creating bots for Slack. With hanu you can get started with the buzzword ChatOps in seconds. The final bot will be running on Heroku using a worker dyno, but of course this works fine on your local machine as well.
One key to Slack’s great success is for sure the easy API and good documentation. All we need to connect the hanu bot to Slack is an API token!
Create a token for the Slack API
Use your web browser and open your team’s Slack account, in my case that’s heftio.slack.com for example and click on the team name in the upper left corner. Choose Apps & Intergrations and Slack will present you the default integrations in the so-called App Directory.
Click on Build in the upper right corner and select to create a custom integration. Slack will show you a couple of options and as we want to connect a bot using the Slack Real Time Messaging API you should select corresponding option:
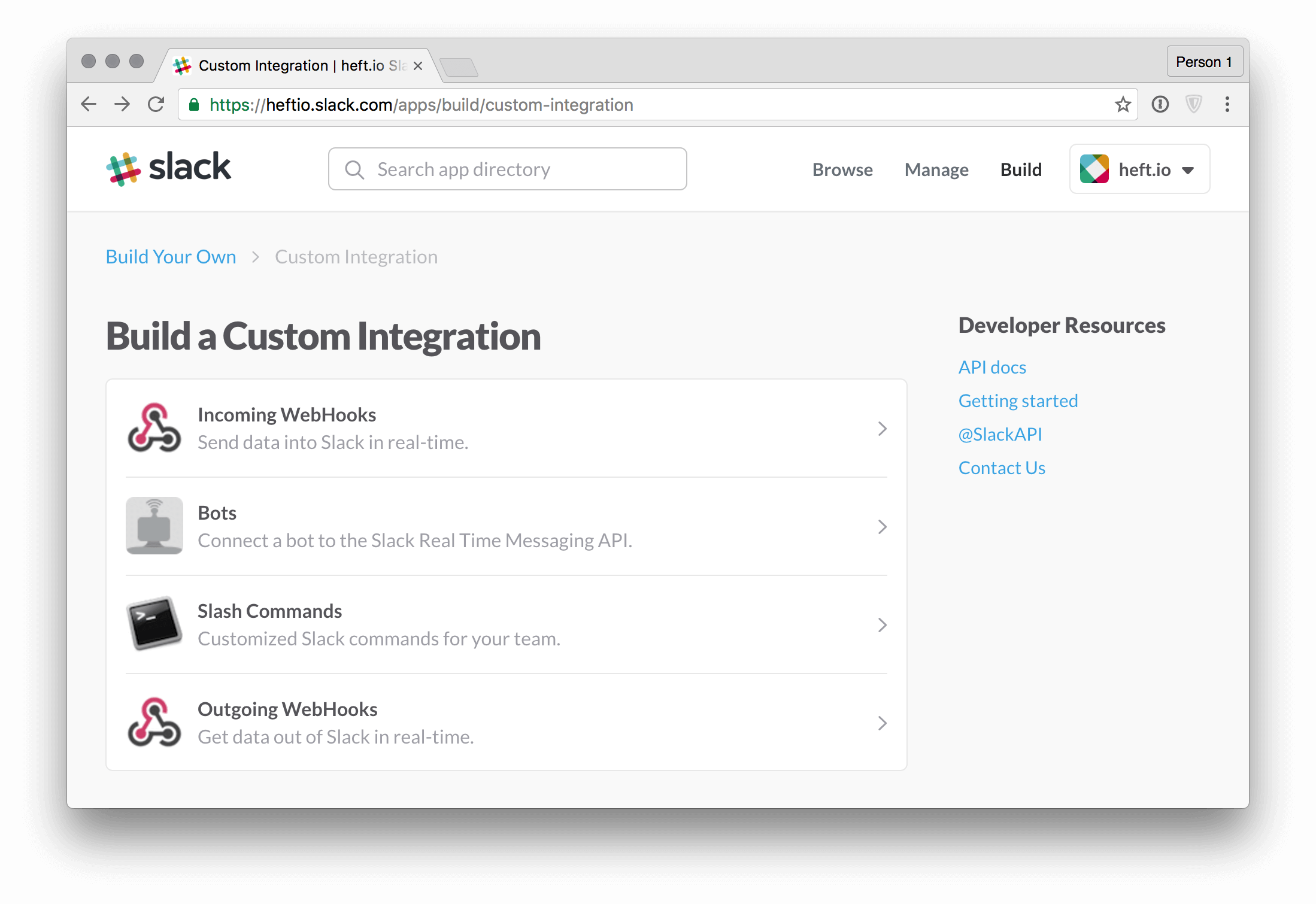
Follow the next steps in the Slack dialog and choose a name for you bot, upload an image and configure a description which will be shown in your bot’s profile. And write down the bot’s API token of course! This will be needed for connecting hanu to the Slack API.
Hanu example code from GitHub
The hanu repository includes an example usage in the README.md which is all we need to use with the API token and start a bot with three custom commands.
Create a new directory somewhere, let’s call it hanu-example and put a file named main.go with the following content into the folder:
package main
import (
"log"
"strings"
"github.com/sbstjn/hanu"
"github.com/sbstjn/hanu/conversation"
)
func main() {
slack, err := hanu.New("YOUR_SLACK_TOKEN")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
Version := "0.0.1"
slack.Command("shout <word>", func(conv conversation.Interface) {
conv.Reply(strings.ToUpper(conv.Param("word")))
})
slack.Command("whisper <word>", func(conv conversation.Interface) {
conv.Reply(strings.ToLower(conv.Param("word")))
})
slack.Command("version", func(conv conversation.Interface) {
conv.Reply("Thanks for asking! I'm running `%s`", Version)
})
slack.Listen()
}
Replace YOUR_SLACK_TOKEN with the token Slack showed to you during the setup of the bot and you are done. Now install the needed dependencies and you can start the bot and begin chatting!
$ > cd /path/to/your/hanu-example
$ > godep save
$ > go run main.go
As soon as you run the main.go file, you should notice the little dot beside the bot’s username in Slack changing from grey to green, indicating our bot is online.
Register Slackbot commands with hanu
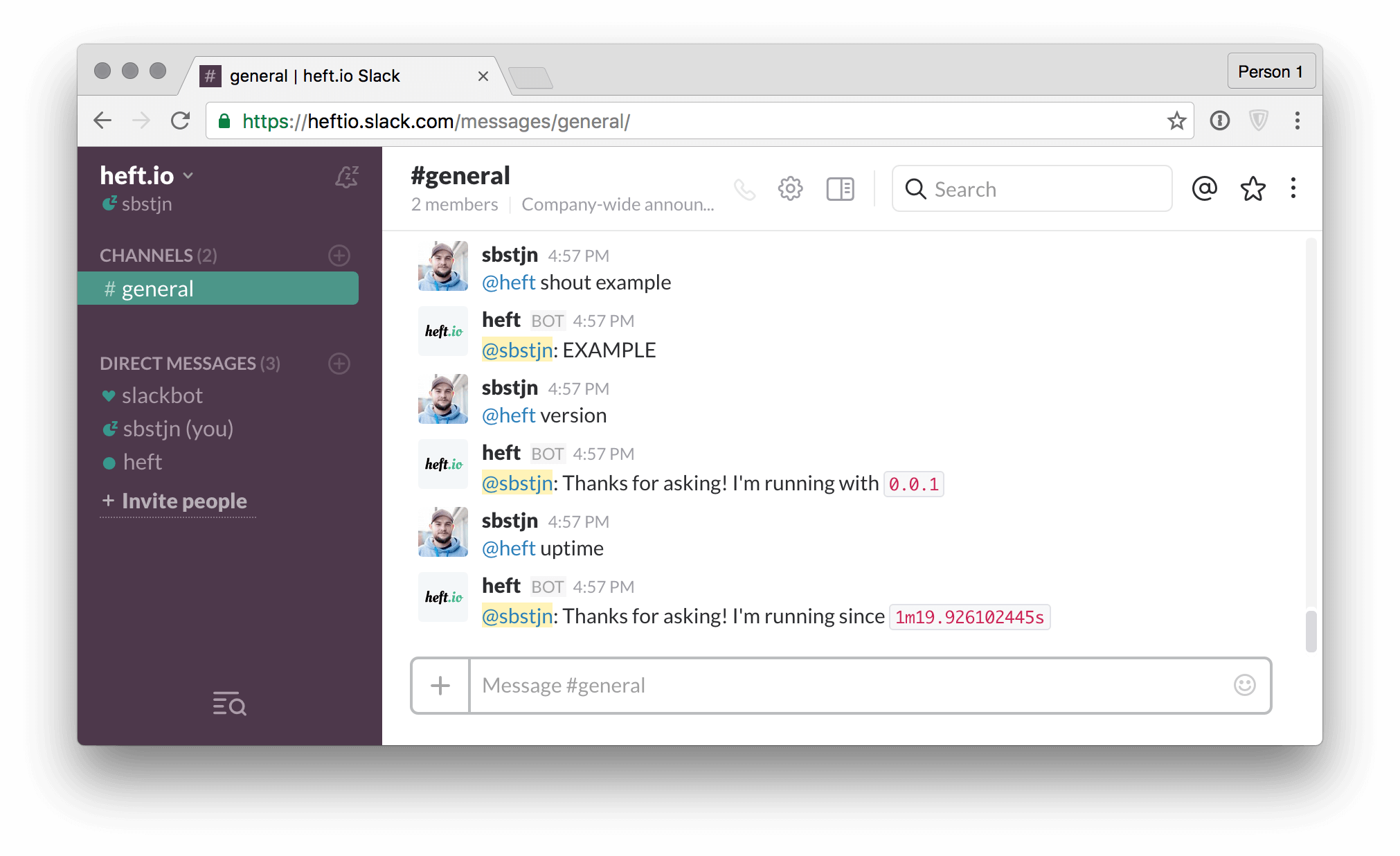
The example code above configures three commands and hanu comes with a built-in help command, which will reply to help requests with a list of all available commands:
shout <word>whisper <word>version
You can communicate with your bot using direct messages and mentions as well. The reply from the bot will of course include your username to identify the response to your request if you have multiple users requesting tasks from your bot.
As said before, hanu auto-generates a command overview. Whenever you ask the bot for help it will show you a list of available commands with a description, when configured:
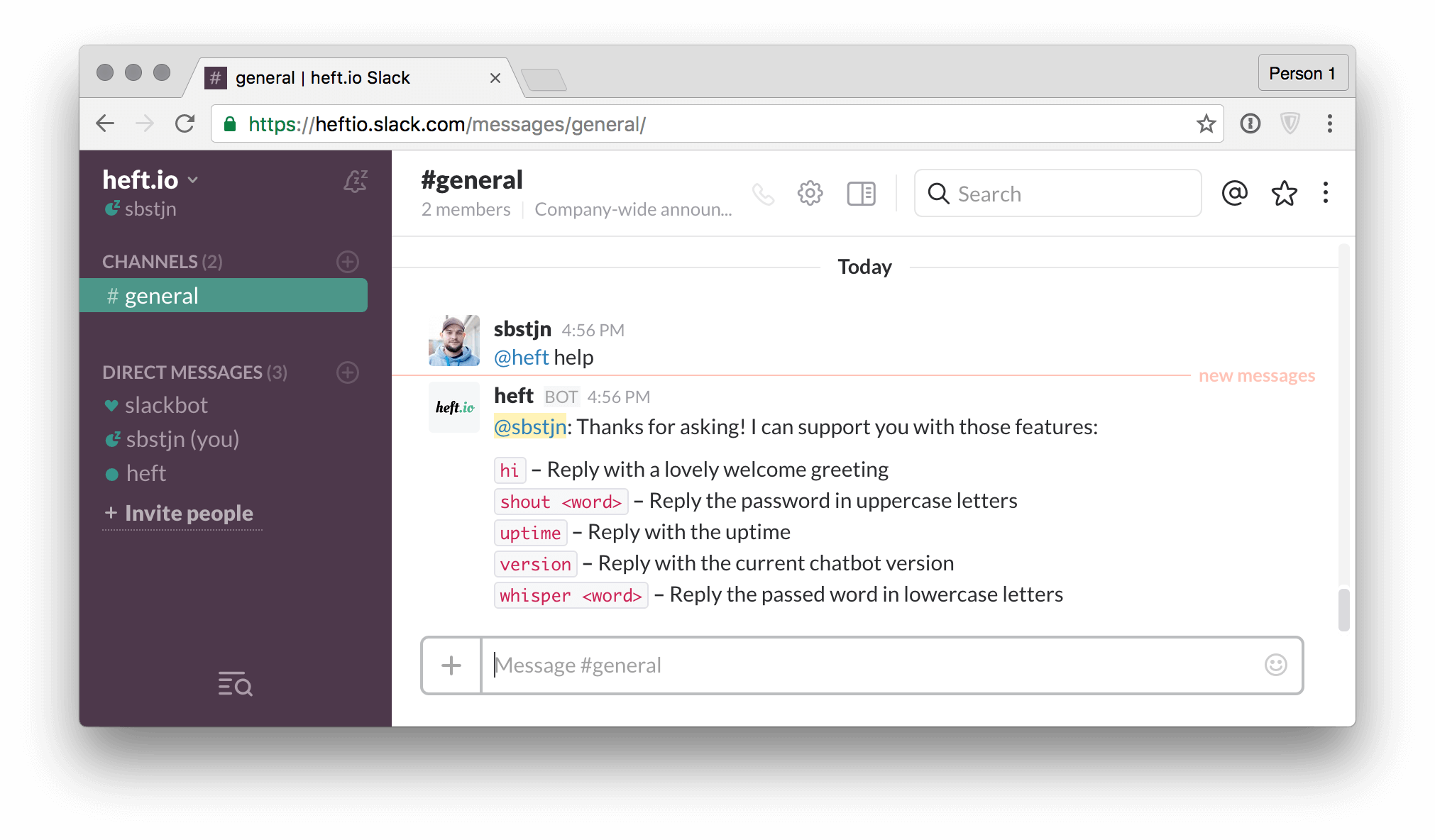
The example code from hanu’s README.md uses the minimal setup for a bot’s command. To learn more about commands and their descriptions you should have a look at the detailed hanu-example project on GitHub …
Deploy your Slackbot to Heroku
Thanks to hanu your bot will work fine on Heroku and the hanu-example project is already prepared to be used as on worker dyno! Just create your Heroku application, configure your Slack API Token as an environent variable in Heroku and scale up your dyno to connect your bot to the Slack API:
$ > git clone git@github.com:sbstjn/hanu-example.git
$ > cd hanu-example
$ > heroku create
$ > heroku config:set HANU_EXAMPLE_SLACK_TOKEN=YOUR_TOKEN
$ > git push heroku master
$ > heroku ps:scale worker=1
Scaling dynos... done, now running worker at 1:Hobby
That’s all. Your bot runs perfectly on Heroku now!
I would love to hear your feedback on hanu! Pull requests are always welcome, as well as feedback on twitter. Just message me and let’s talk about hanu …